Aluminum Casting Process Comparison
2. High Pressure Die Casting - In this process, the liquid metal is injected at high speed and high pressure into a metal mould. A schematic view of high pressure die casting is given in below Figure.
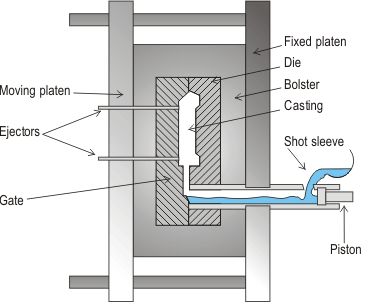
This equipment consists of two vertical platens on which bolsters are located which hold the die halves. One platen is fixed and the other can move so that the die can be opened and closed. A measured amount of metal is poured into the shot sleeve and then introduced into the mould cavity using a hydraulically-driven piston. Once the metal has solidified, the die is opened and the casting removed.
In this process, special precautions must be taken to avoid too many gas inclusions which cause blistering during subsequent heat-treatment or welding of the casting product.
Both the machine and its dies are very expensive, and for this reason pressure die casting is economical only for high-volume production.
This equipment consists of two vertical platens on which bolsters are located which hold the die halves. One platen is fixed and the other can move so that the die can be opened and closed. A measured amount of metal is poured into the shot sleeve and then introduced into the mould cavity using a hydraulically-driven piston. Once the metal has solidified, the die is opened and the casting removed.
In this process, special precautions must be taken to avoid too many gas inclusions which cause blistering during subsequent heat-treatment or welding of the casting product.
Both the machine and its dies are very expensive, and for this reason pressure die casting is economical only for high-volume production.
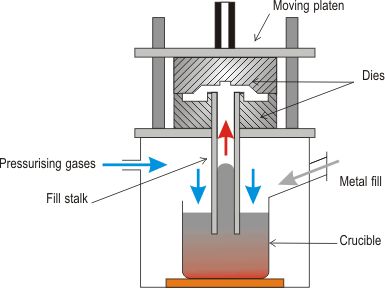
3. Low Pressure Die Casting - As schematised in below Figure, the die is filled from a pressurised crucible below, and pressures of up to 0.7 bar are usual. Low-pressure die casting is especially suited to the production of components that are symmetric about an axis of rotation. Light automotive wheels are normally manufactured by this technique.
2. Sand casting(Aluminum alloy)
The sand cast method consists of a furan resin bonded sand model into which melted metal is poured at about 750°C. The furan resin reacts at room temperature with acid mixed with the sand. As material for the casting pattern are aluminum and wood, it is a relatively low cost.
Sand casting is suitable for relatively large castings used in small or medium quantities. The casting method is often used also for prototype manufacturing. The surface finish and casting tolerances are adequate for most purposes.
3. Gravity die casting(Aluminum alloy)
In gravity die casting molten aluminum is poured into a metallic tool. The casting temperature is about 750°C. The tolerances and surface finish are good. The use of sand cores enables casting of very complex components.
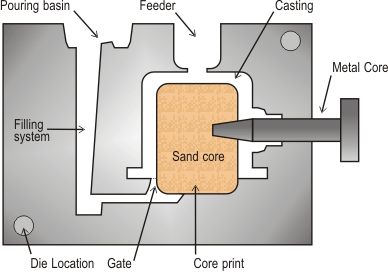
Gravity die casting method is competitive when the lot size is relatively small or when heat treatment is needed to improve the mechanical properties. This casting method gives better tolerances and surface finish than sand casting. The tooling costs are somewhat higher than by sand casting